Transfer Case Explained: This One Part Could Be Destroying Your Drivetrain
Introduction
In 4WD and AWD vehicles, the transfer case is a critical component that’s often overlooked—until problems arise. When it malfunctions, it doesn’t just impair your vehicle’s performance; it can trigger a cascade of drivetrain issues that result in major repair bills. Whether you’re a daily commuter, an off-road enthusiast, or someone who frequently tows heavy loads, understanding the transfer case can protect your vehicle and wallet. This article breaks down everything you need to know—from basic functions and types to maintenance tips, symptoms of failure, and answers to frequently asked questions.
What Is a Transfer Case?
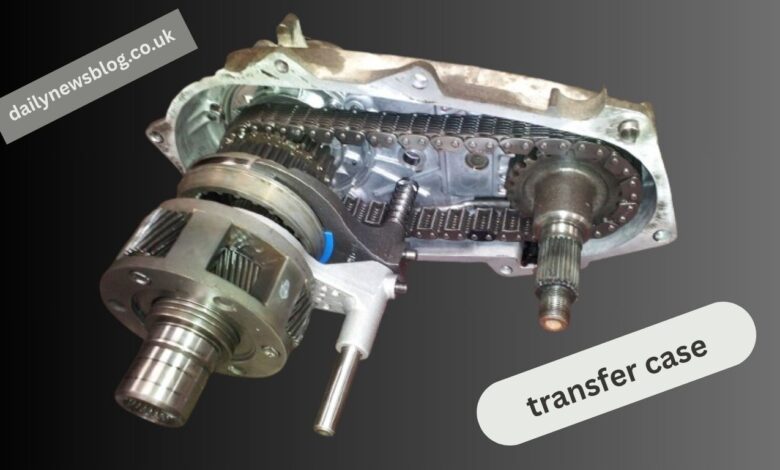
A transfer case is a part of the drivetrain used in vehicles with multiple driven axles. It’s responsible for splitting power from the transmission and delivering it to the front and rear axles through driveshafts. In essence, it enables your vehicle to switch from two-wheel drive to four-wheel drive and manage torque distribution when in motion.
Many modern transfer cases also house low-range gearing, which is essential for off-road driving. These lower gears allow the vehicle to crawl slowly over rocks or steep terrain with greater control and torque. Without a functioning transfer case, even the most powerful engine and transmission won’t be able to distribute that power effectively to all wheels.
How Does a Transfer Case Work?
The transfer case operates by taking rotational force from the transmission and using a set of gears or a chain-driven system to send torque to the front and rear axles. Some systems are mechanically operated, while others are electronically controlled. In many cases, torque distribution is managed dynamically to provide traction where it’s needed most.
Transfer cases also include synchronization mechanisms, which help shift smoothly between modes, such as from 2WD to 4WD High or 4WD Low. The electronics involved in newer systems allow the driver to toggle between these modes with a push of a button or turn of a dial, enhancing ease of use. Some advanced systems even engage automatically depending on traction conditions.
Types of Transfer Cases
Part-Time vs Full-Time Transfer Cases
Part-time transfer Cases are commonly found in trucks and off-road SUVs. These systems operate in 2WD most of the time but can be shifted into 4WD manually. They are not meant to be used on dry pavement while in 4WD, as they lack a center differential to account for differences in wheel rotation.
Full-Time Transfer Cases, on the other hand, continuously power all four wheels. They include a center differential or clutch pack that allows for different speeds between the front and rear axles, making them safe for all-road driving conditions, including dry pavement.
Manual vs Electronic Shift Transfer Cases
Older vehicles feature manual transfer cases, which require physically shifting a lever, often located next to the gear shifter. This mechanical approach is rugged and reliable but less convenient.
Electronic shift transfer cases use dashboard controls and electric motors to switch modes. While more user-friendly, they rely on sensors and actuators that can malfunction, particularly in harsh environments.
Active and On-Demand Transfer Cases
Some high-end or crossover vehicles use active or on-demand transfer cases. These use sensors and computer systems to automatically distribute torque based on traction needs, improving both safety and fuel efficiency.
Symptoms of a Bad Transfer Case
Grinding or Unusual Noises
If you hear grinding, whining, or clunking while driving—especially when shifting drive modes—it may be a sign of internal gear damage or low fluid levels.
Difficulty Shifting Between Modes
A healthy transfer case should shift smoothly. If it hesitates or fails to switch between 2WD and 4WD, the internal shift forks, actuator motors, or control modules could be failing.
Fluid Leaks and Burnt Odors
Leaking transfer case fluid can be identified by reddish or amber fluid under the vehicle. Burnt smells may indicate overheating due to a lack of lubrication.
Vibration or Jerky Movement
Unusual vibrations or jerky handling while driving could be symptoms of a failing transfer case or mismatched torque distribution between axles.
Dashboard Warning Lights
Many modern vehicles will alert you with a “Service 4WD” or “Check Drivetrain” warning if the system detects transfer case issues. These alerts should not be ignored.
Common Causes of Transfer Case Failure
Several factors can contribute to transfer case failure, including:
- Improper use: Engaging 4WD on dry pavement in part-time systems causes binding and excessive wear.
- Neglected maintenance: Dirty or old fluid can degrade internal components and cause overheating.
- Overloading: Towing beyond the vehicle’s capacity strains the transfer case.
- Electrical issues: In vehicles with electronic shift systems, failed sensors or modules can mimic mechanical failure.
Weather conditions also play a role. Cold climates can thicken transfer case fluid, while hot weather may accelerate fluid degradation, both increasing the risk of failure if maintenance is skipped.
How to Maintain a Transfer Case
Recommended Fluid Change Intervals
Most automakers recommend changing the transfer case fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles. However, if you tow frequently or drive off-road, you may need to change it more often.
What Type of Fluid to Use
Using OEM-approved fluid is crucial. Each transfer case is engineered with specific fluid tolerances. Using incorrect fluid can lead to slipping, overheating, or component failure.
DIY vs Professional Maintenance
DIY fluid changes are possible with basic tools, a drain pan, and the correct replacement fluid. However, diagnosing internal damage or rebuilding a transfer case is best left to professionals.
Regular inspections—especially before off-road trips or long hauls—can catch issues early. Look for leaks, strange sounds, or any difficulty in shifting.
Repair or Replace? What to Do When a Transfer Case Fails
If your transfer case has minor issues, like a leaky seal or a worn actuator, repair is often economical. But internal damage like broken gears or cracked housings often requires a rebuild or full replacement.
Transfer Case Replacement Costs
- Minor repairs: $300–$800
- Rebuild: $1,000–$1,800
- Replacement (new or remanufactured): $1,500–$2,500+
Choosing between repair and replacement depends on the age of your vehicle, the extent of damage, and future reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens when a transfer case goes bad?
It can result in a loss of 4WD capability, increased noise, drivetrain damage, and poor handling. In severe cases, it may prevent the vehicle from moving at all.
What is a transfer case?
A transfer case is a drivetrain component that splits engine power between the front and rear axles in AWD and 4WD vehicles.
How much does it cost to replace a transfer case?
Replacement typically costs between $1,500 and $2,500, depending on labor, vehicle make, and whether the unit is new or remanufactured.
What are the three types of transfer cases?
- Part-Time Transfer Case
- Full-Time Transfer Case
- On-Demand (Active) Transfer Case
Can I drive with a bad transfer case?
It’s not advisable. Driving with a failing transfer case can lead to loss of control or catastrophic drivetrain failure, leaving you stranded or causing further damage.
Can a transfer case be repaired?
Yes. Minor issues like leaks, sensors, or actuators can be repaired. Severe internal damage may require a rebuild or replacement.
Conclusion
The transfer case may not be something you think about daily, but it’s vital to your vehicle’s ability to function in tough conditions. Ignoring early warning signs or skipping fluid maintenance can lead to a domino effect of drivetrain issues, turning a simple fix into a multi-thousand-dollar disaster.
This one part could be destroying your drivetrain without you even knowing it. Take the time to inspect, maintain, and repair your transfer case when needed. Whether you’re an off-road warrior or a winter commuter, keeping your transfer case healthy ensures your vehicle stays reliable, safe, and road-ready.
CLICK HERE Dailynewsblog




