What is a Rheometer and How Does it Work?
Learning about the flow and deformation of materials is relevant when it comes to the study of such materials as rubber, plastics, or liquids. This is where a rheometer is introduced. It assists in the determination of the behavior of a material under stress or strain.
Simply put, a rheometer is a device for determining the movement of a material once pressure is put into it. Let us discuss what is a rheometer?, its working, the types, and the high importance of a Rheometer in industries.
What is a Rheometer?
A rheometer is a scientific equipment used to estimate the flow and movement of materials. It is an expression of how viscous or rigid a substance is when put under pressure or rotated.
Rheology refers to the study of flow. That is why a rheometer is a device that is employed in the rheology study to learn the flow characteristics of liquids and semi-solids.
It is extensively applied to all industries such as rubber, food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals in order to have consistent, as well as quality products.
Why Is a Rheometer Important?
A rheometer makes the scientists and manufacturers aware of how materials behave in the real world. There are aspects such as the extent to which a rubber compound stretches or the spread of a cream on the skin.
Experts can also determine how rubber cures and how it gets strong using such equipment as the OTS Technik Vulcanized Rubber Rotorless Rheometer. The information is useful in choosing the appropriate material, formulas, and quality of products.
Performances of a Rheometer.
- Measure Viscosity
It narrates the way thick or thin a liquid becomes as a force is exerted on it.
- Measure Elasticity
It demonstrates the recovery of a material after deformation.
- Check Shear Rate
It is used to determine the response of different materials to varying speeds or forces.
- Monitor Curing Process
Rheometers are used in particular with the rubber industry, where the hardness of rubber can be monitored as a function of heat.
- Quality Control
It makes sure that all kinds of material act in a similar manner of production.
How Does a Rheometer Work?
A rheometer operates by straining a material and imposing stress on it, and recording the received response. It normally contains two plates or cones, one immobile and one moving.
Between them is a little sample of the material. As one of the plates slides across or swivels, the rheometer will document the resistance or flow of the material.
The rheometers available today come with fancy software and sensors that display the information on the viscosity, elasticity, and time-correlation of behavior.
OTS Technik Vulcanized Rubber Rotorless Rheometer utilises this principle but is specifically made to test rubber. It quantifies torque and time to verify the way rubber is cured and obtain strength.
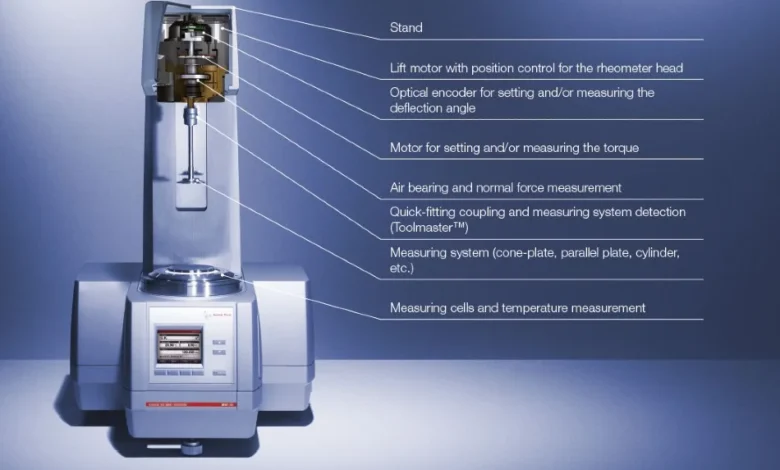
The Major Elements of a Rheometer.
- Motor – gives an alternation movement, or rotation.
- System – typically, some cone, plate, or cylinder arrangement.
- Temperature Control Unit – maintains the temperatures of testing conditions at a constant.
- Torque Sensor – indicates the resistance in the sample.
- Computer Interface– shows graphs and results in real-time.
All the parts are combined to provide accurate and reproducible information regarding material properties.
Types of Rheometers
It has two chief types: rotational rheometers and capillary rheometers.
Rotational Rheometers:
They place a twisting force on the specimen. These do well at testing liquids, creams, and pastes.
Capillary Rheometers:
These force the material through a very small tube in order to determine flow. The plastics and the rubber materials are sent through them.
There are also specialized models, such as the OTS Technik Vulcanized Rubber Rotorless Rheometer, which is designed to experiment with the vulcanization of rubber with no rotor. This enhances accuracy and uniformity of findings.
Applications of Rheometers
Rheometers find application in most industries:
Rubber and Plastic Production – to measure shelf, strength, and flow.
Food Industry – to research texture, thickness, and pourability.
Pharmaceuticals – to test gels, ointments, and liquid medicines.
Cosmetics– to examine creams, lotions, and shampoos.
Chemical Industry – to determine the viscosity of paints, oils, and adhesives.
These applications are used to make sure that all the products feel, spread, and act as desired.
Advantages of Rheometer Use.
Rheometer offers specific information that will contribute to the enhancement of materials and production. Here are some key advantages:
- Better product consistency
- Reduced waste in production
- Better formulation of materials.
- Accurate process control
- Faster quality checks
This kind of performance and reliability advantage is an advantageous quality control that industries possess as a result of such data.
The Future of the Rheometer Technology.
Rheometers are becoming more intelligent and automated. They can test several samples simultaneously and analyze them in real-time.
The digital systems can now be used to monitor curing and viscosity curves in real time. One such advanced machine is the OTS Technik Vulcanized Rubber Rotorless Rheometer, which is applicable in both research laboratories and production facilities all over the world.
Conclusion
A rheometer is a very powerful instrument that quantifies the flow and changes of materials under the influence of stress. It is significant in controlling quality, research, and design of products.
Knowing what a rheometer is also enables industries to make the most reliable materials. OTS Technik Vulcanized Rubber Rotorless Rheometer is unique in its exactness in the testing of rubber and in the processes following.
The rheometer makes sure that all of the products can do their job properly, whether it is rubber, cosmetics, or food production; each product is consistently as powerful as it is supposed to be, and it is reliable as well.




